Union Transform
The Union transform enables you to combine multiple datasets vertically by appending rows from different sources into a single dataset. This transform provides several options for aligning columns and handling discrepancies between input datasets.
Basic Usage
To union multiple datasets:
The Union transform requires at least two Data Input nodes.
Make sure you have added two datasets to your pipeline before using this operation.
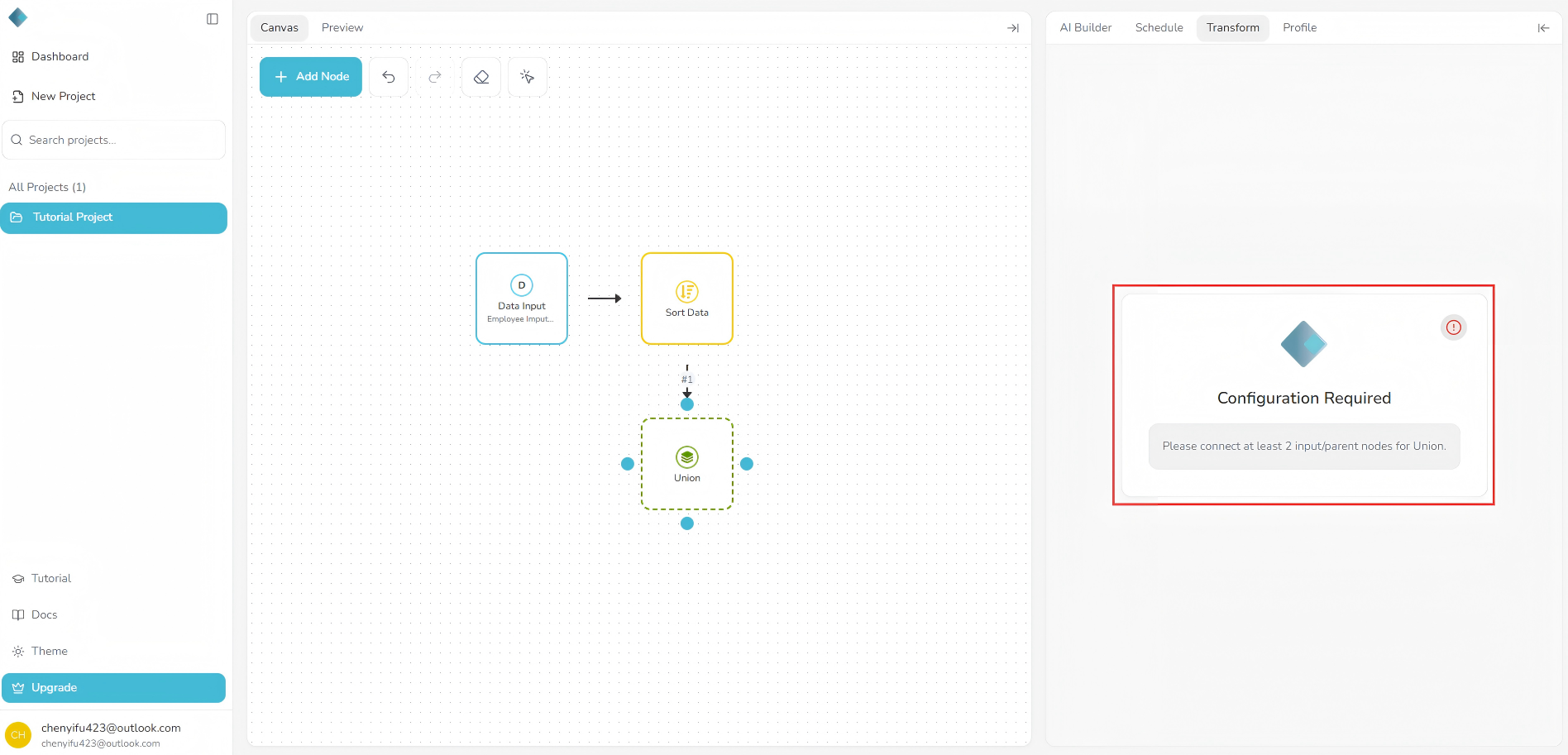
- Select the Union transform from the transform menu.
- Choose the datasets you want to union.
- Configure the alignment mode and additional options.
- (Optional) Adjust advanced settings for more control.
Configuration Options
Basic Options
-
Alignment Mode: Choose how columns from different datasets will be aligned:
Name: Align columns based on their names.Position: Align columns based on their order in each dataset.Manual: Manually map columns between datasets.
-
Output Order: Drag and drop to reorder the datasets in the final output.
-
Common Columns Only: Enable this option to include only columns present in all input datasets.
Advanced Options
-
Manual Column Mapping: When using
Manualalignment mode, specify how columns from each dataset should be mapped. -
Column Configuration: Manually configure which fields to include and how they should be aligned.
-
Warn on Extra Columns: Receive warnings about columns that are not present in all input datasets.
Examples
Here are some examples of how to use the Union transform:
Example 1: Name-based Alignment
Input Datasets:
Dataset 1:
| A | B |
|---|---|
| 1 | x |
| 2 | y |
Dataset 2:
| B | C |
|---|---|
| z | 3 |
| w | 4 |
Configuration:
- Alignment Mode:
Name - Common Columns Only:
Off
Result:
| A | B | C |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | x | null |
| 2 | y | null |
| null | z | 3 |
| null | w | 4 |
Example 2: Position-based Alignment
Input Datasets:
Dataset 1:
| A | B |
|---|---|
| 1 | x |
| 2 | y |
Dataset 2:
| C | D |
|---|---|
| 3 | z |
| 4 | w |
Configuration:
- Alignment Mode:
Position - Common Columns Only:
Off
Result:
| A | B |
|---|---|
| 1 | x |
| 2 | y |
| 3 | z |
| 4 | w |
Example 3: Manual Alignment
Input Datasets:
Dataset 1:
| Name | Age |
|---|---|
| John | 30 |
| Mary | 25 |
Dataset 2:
| Full Name | Years |
|---|---|
| Bob Smith | 40 |
| Alice Lee | 35 |
Configuration:
- Alignment Mode:
Manual - Manual Mapping:
- Name → Full Name
- Age → Years
Result:
| Full Name | Years |
|---|---|
| John | 30 |
| Mary | 25 |
| Bob Smith | 40 |
| Alice Lee | 35 |
When working with datasets that have different column names but represent the same information, use the Manual alignment mode for precise control over how columns are combined.
Be cautious when using Position-based alignment with datasets that have different structures. Columns might be misaligned if their order differs across datasets.
Best Practices
-
Verify Column Alignment: Always double-check that columns are aligned correctly, especially when using
Position-based alignment. -
Handle Missing Data: If
Common Columns Onlyis disabled, missing columns may introduce null values in the result. -
Use Output Order: Reorder input datasets as needed to prioritize data from specific datasets in the output.
-
Monitor Warnings: Pay attention to warnings about extra columns to ensure no data is unintentionally omitted.
-
Test with Samples: For large datasets, test with smaller samples first to ensure your union configuration works as expected.